What is the position of foramen of magendie, foramen magnum and luschka?
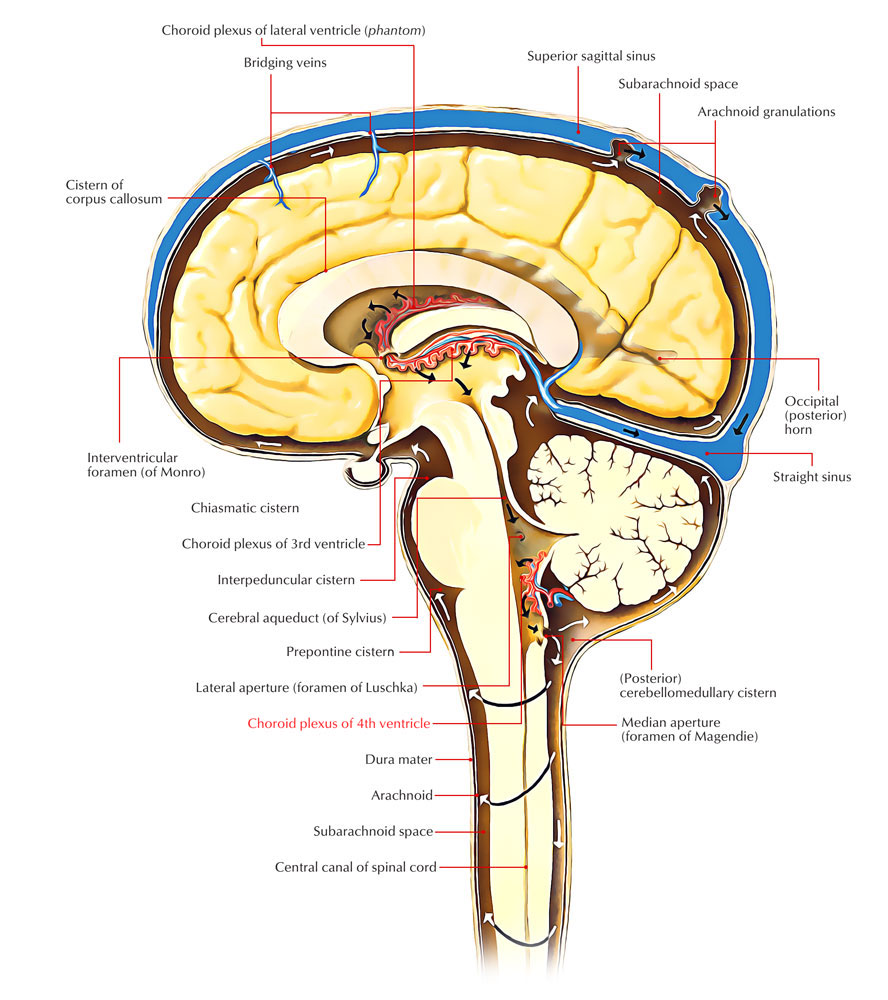
The medial aperture of the fourth ventricle (foramen of Magendie), is situated immediately above the inferior angle of the ventricle. The lateral apertures (foramina of Luschka) are found at the extremities of the lateral recesses. By means of these three openings the ventricle communicates with the subarachnoid cavity, and the cerebrospinal.

4th ventricle of brain Dentowesome
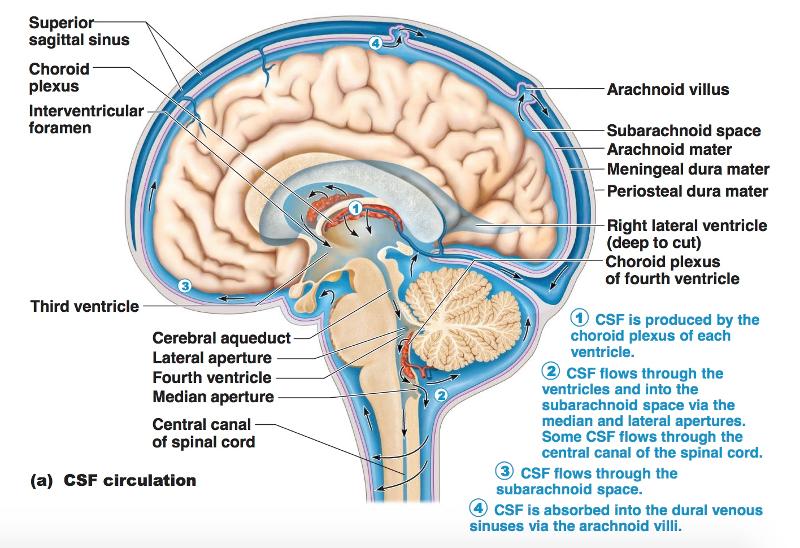
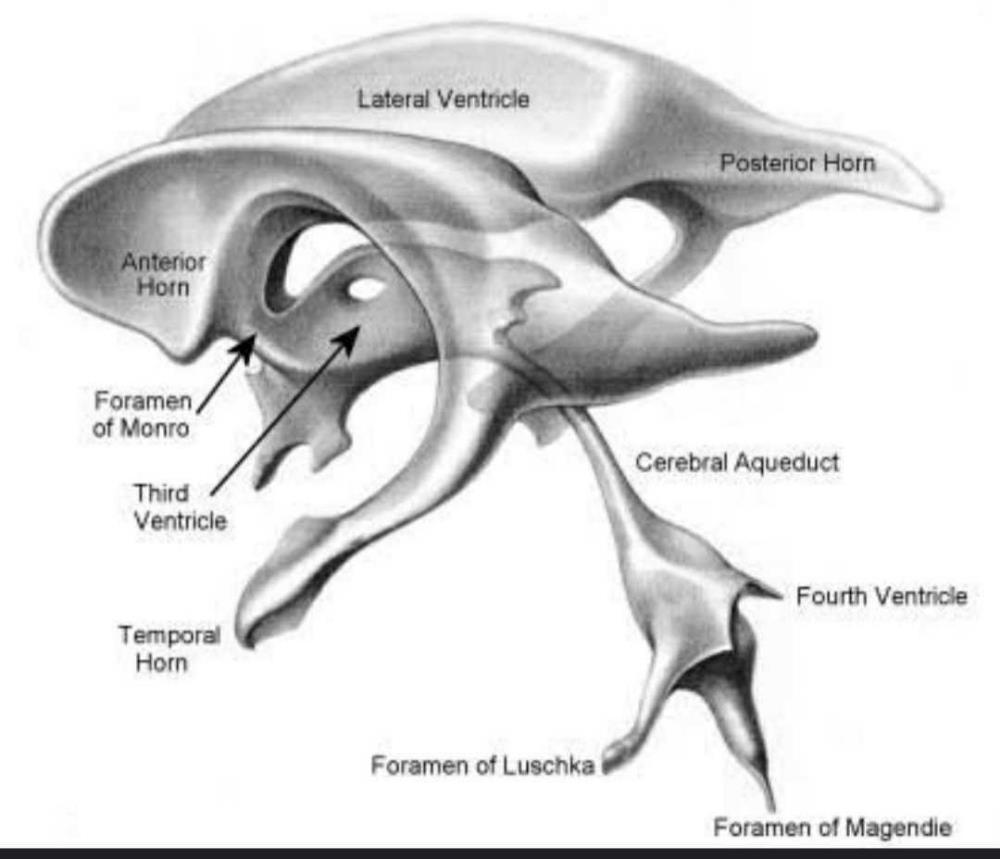
The ventricular system is comprised of four interconnected CSFfilled, ependymal-lined cavities that lie deep within the brain. The paired lateral ventricles communicate with the third ventricle via the Y-shaped foramen of Monro. The third ventricle communicates with the fourth ventricle via the cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius).
ventricular system overview Brain Imaging
The foramen of Luschka and Magendie may be obstructed in a condition called Arnold-Chiari malformation where the cerebellar tonsils get displaced downward through the foramen magnum and can give rise to internal hydrocephalus. They can also be obstructed in the case of inflammatory fibrosis of the meninges leading to congenital hydrocephalus.
Chapter 12 The CNS (Brain and Spinal Cord) Flashcards Easy Notecards
The foramen of Magendie (aka median aperture) is a single midline structure within the ventricular system of the brain which connects the fourth ventricle with the cerebellopontine cistern. It represents one of the three pathways that enable CSF to connect with the subarachnoid space. It lies posterior to the pons and anterior to the cerebellum.
What is the position of foramen of magendie, foramen magnum and luschka?
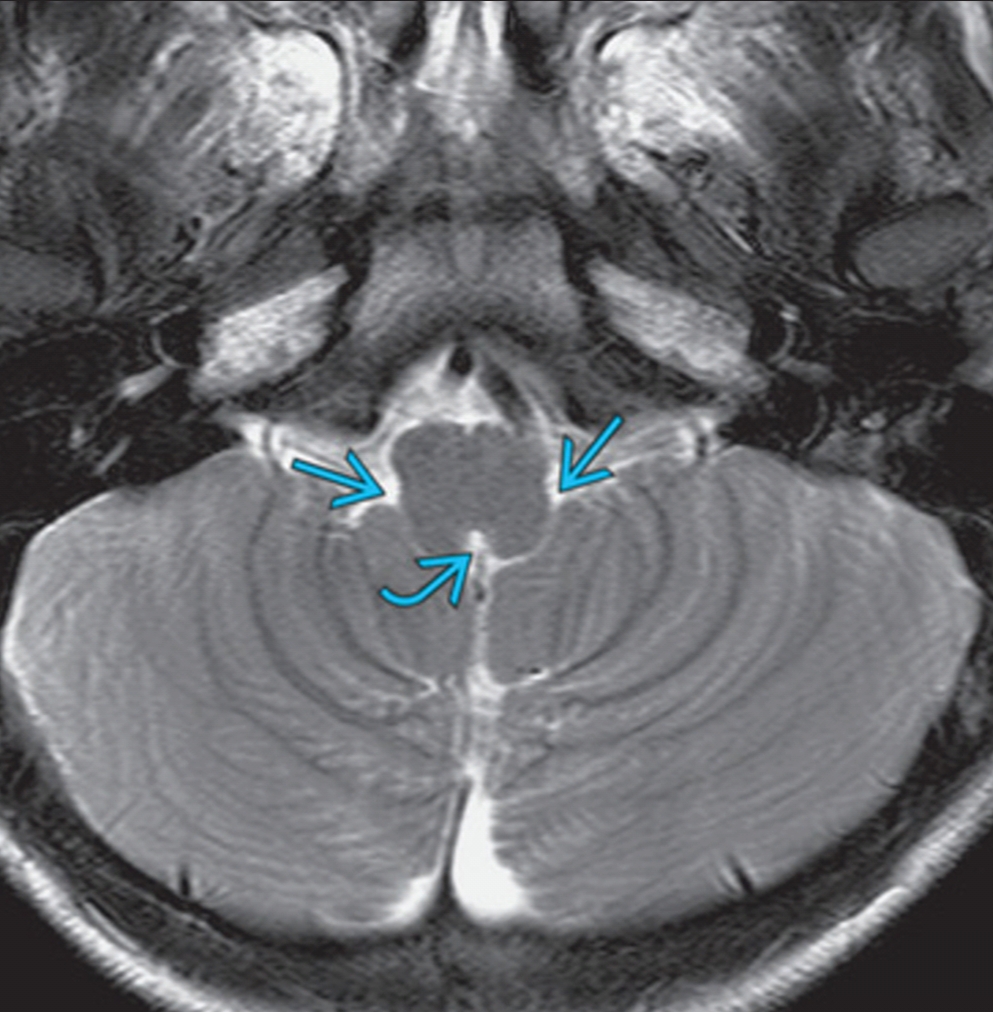
The irregularly shaped foramen of Magendie is located in the caudal sloping roof of the ventricle (Figs. 6.4 and 6.10). Although the roof of the caudal part of the fourth ventricle and the lateral recesses is composed of tela choroidea, the rostral boundaries of this space are formed by brain structures. These include the cerebellum (covering.
Foramen of magendie hires stock photography and images Alamy
The meaning of FORAMEN OF MAGENDIE is a passage through the midline of the roof of the fourth ventricle of the brain that gives passage to the cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles to the subarachnoid space.

PPT CSF and Ventricular System PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Median aperture (Magendie): fourth ventricle -> subarachnoid space Right & left lateral aperture (Luschka): fourth ventricle -> subarachnoid space: Clinical relations:. exits the fourth ventricle to either enter the central canal of the spinal cord or by the foramina of Luschka and foramen of Magendie to enter the cisterns.
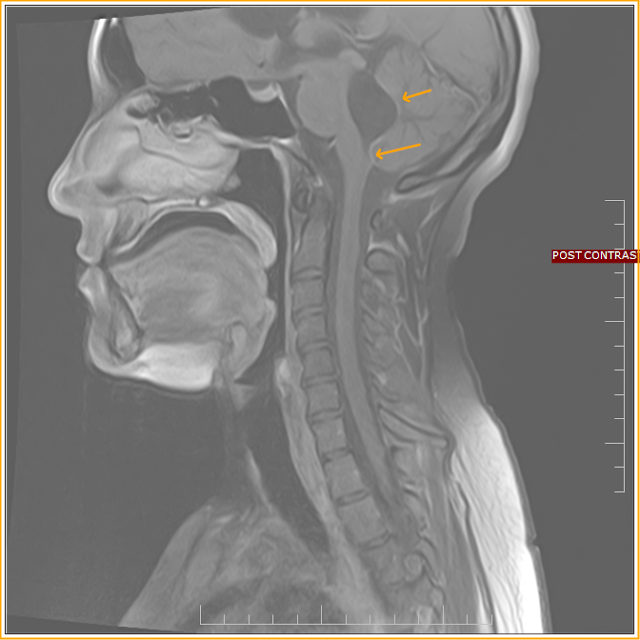
Obstruction of Magendie's Foramen MRI Sumer's Radiology Blog
The foramen of Magendie (aka median aperture) is a single midline structure within the ventricular system of the brain which connects the fourth ventricle with the cerebellopontine cistern. It represents one of the three pathways that enable CSF to connect with the subarachnoid space. It lies posterior to the pons and anterior to the cerebellum.
The cerebrospinal fluid passes out from the ventricle of medulla
Fourteen cases demonstrated extension of tumor into foramen of Magendie or Luschka. Conclusion. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest collection of 4th ventricular subependymomas with imaging findings reported to date. All patients in this cohort had tumors originating between the bottom of the body of the 4th ventricle and the obex.
Choroid Plexus Earth's Lab
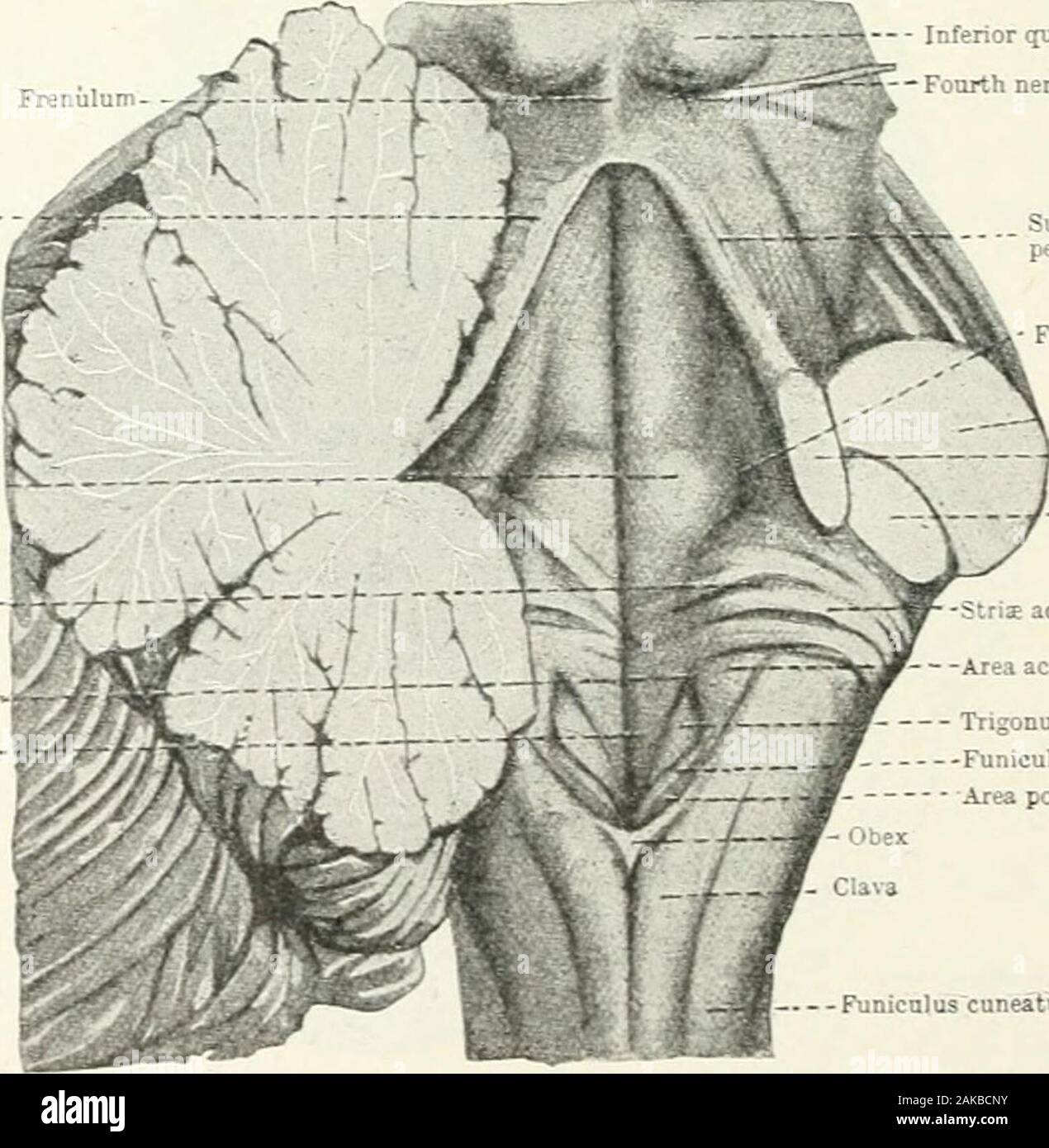
The Foramen of Magendie, a midline opening in the inferior medullary velum, is one of three openings (the other two are the paired lateral foramina of Luschke) that drain CSF from the IV ventricle into the foramen magnum. The posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA), seen prominently on the left side of the image, is a branch of the.
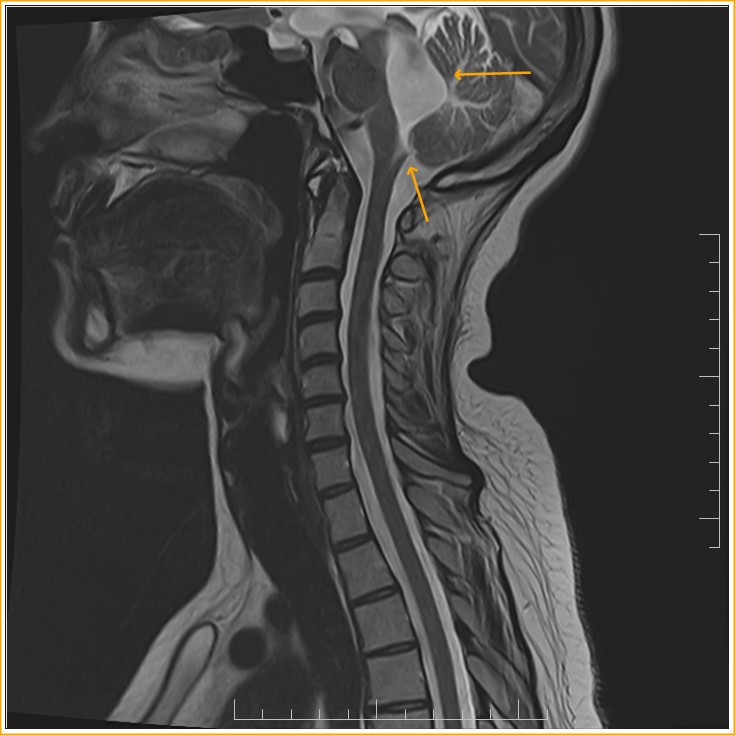
Obstruction of Magendie's Foramen MRI Sumer's Radiology Blog
The discovery of these openings in the 4 th ventricle, first described in the 19 th century by François Magendie and Hubert von Luschka, resulted from continued and tenacious research on the subject. 1 , 2 These openings aroused interest for their importance under normal conditions, and in several congenital or acquired pathological disorders.

VENTRICLES AND THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID Neupsy Key
The lateral apertures (of Luschka) (also known as the foramina of Luschka) are two of the foramina in the ventricular system and link the fourth ventricle to the cerebellopontine cistern. Together with the median aperture (of Magendie) they comprise two of the three sites that CSF can leave the fourth ventricle and enter the subarachnoid space.

Increased cerebrospinal fluid flow through the foramen of Magendie
The CSF finally leaves the fourth ventricle through the foramen of Magendie and the foramina of Luschka to reach the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain. Each lateral ventricle lies within a cerebral hemisphere. The lateral ventricle, when viewed from the lateral aspects of the brain,.

Obstruction of Magendie's Foramen MRI Sumer's Radiology Blog
François Magendie (6 October 1783 - 7 October 1855) was a French physiologist, considered a pioneer of experimental physiology.He is known for describing the foramen of Magendie.There is also a Magendie sign, a downward and inward rotation of the eye due to a lesion in the cerebellum.Magendie was a faculty at the College of France, holding the Chair of Medicine from 1830 to 1855 (he was.

Foramen The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
The lower part of the membrane has a large aperture, the foramen of Magendie. This is the median aperture of the fourth ventricle, through which the entire ventricular system communicates. [Ventricles of the brain]The lateral ventricles are two C-shaped cavities, one in each cerebral hemisphere. The interventricular foramen (or foramen of Monro.

Organization of the ventricular system of the brain. The brain
The median aperture (also known as the medial aperture, and foramen of Magendie) is an opening of the fourth ventricle at the caudal portion of the roof of the fourth ventricle. [1] It allows flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the fourth ventricle into the cisterna magna. [2] [3] The other two openings of the fourth ventricle are the.